Hydraulics
April 28, 2025
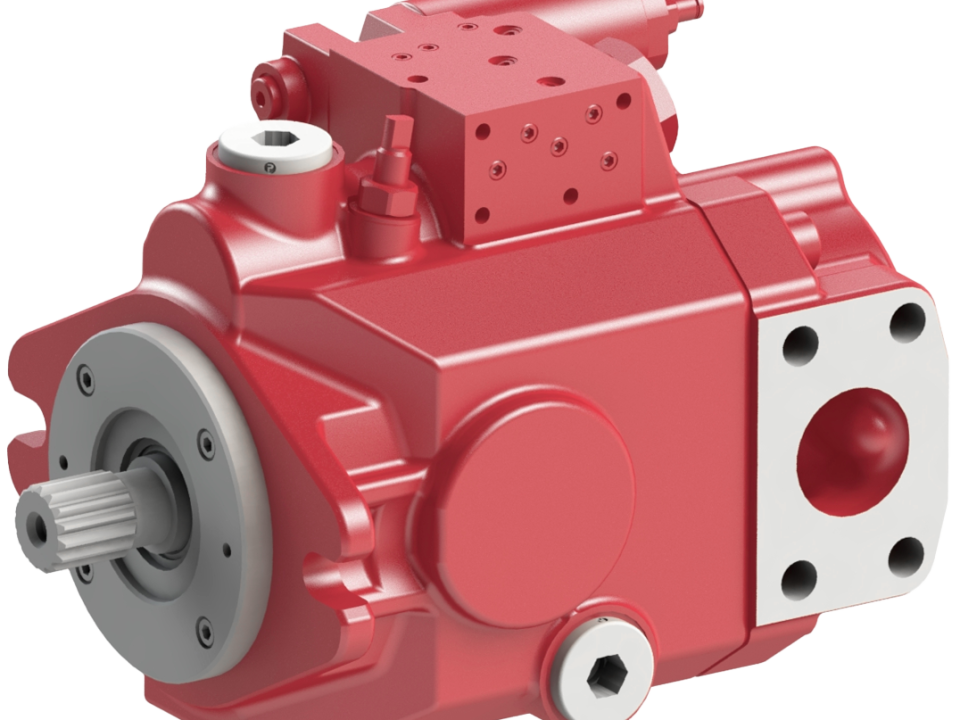
Hydraulic Pumps
April 29, 2025Hydraulic Valves: Principles, Types, and Applications
Introduction
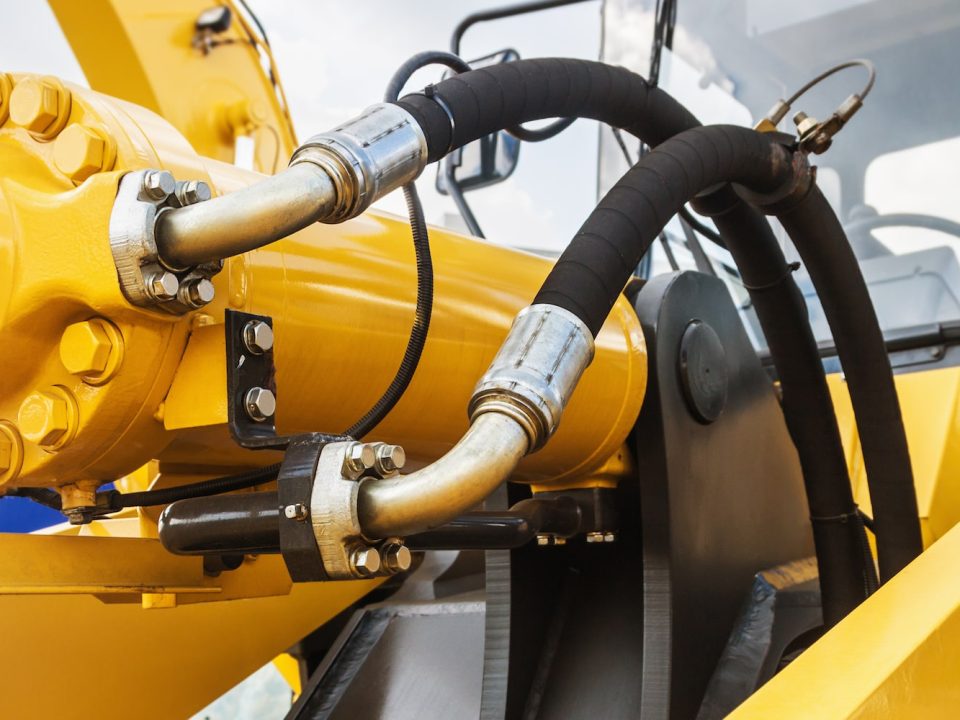
Hydraulic valves are essential components in hydraulic systems, playing a key role in controlling fluid flow, pressure, and direction. These valves act as the “brain” of hydraulic systems, enabling precise control over the operation of machinery and equipment. In this article, we will explore the principles of hydraulic valve operation, their various types, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and the challenges associated with their use.
Principles of Hydraulic Valve Operation
Hydraulic valves operate based on the physical laws governing fluids, providing precise control over hydraulic systems. These valves generally perform three main functions:
- 1. Flow Control: Valves can regulate the amount of fluid flow to control the speed of system operation.
- 2. Pressure Control: Pressure valves are used to adjust and limit system pressure to prevent damage to components.
- 3. Directional Control: Directional valves direct fluid flow to the desired path to create linear or rotary motion.
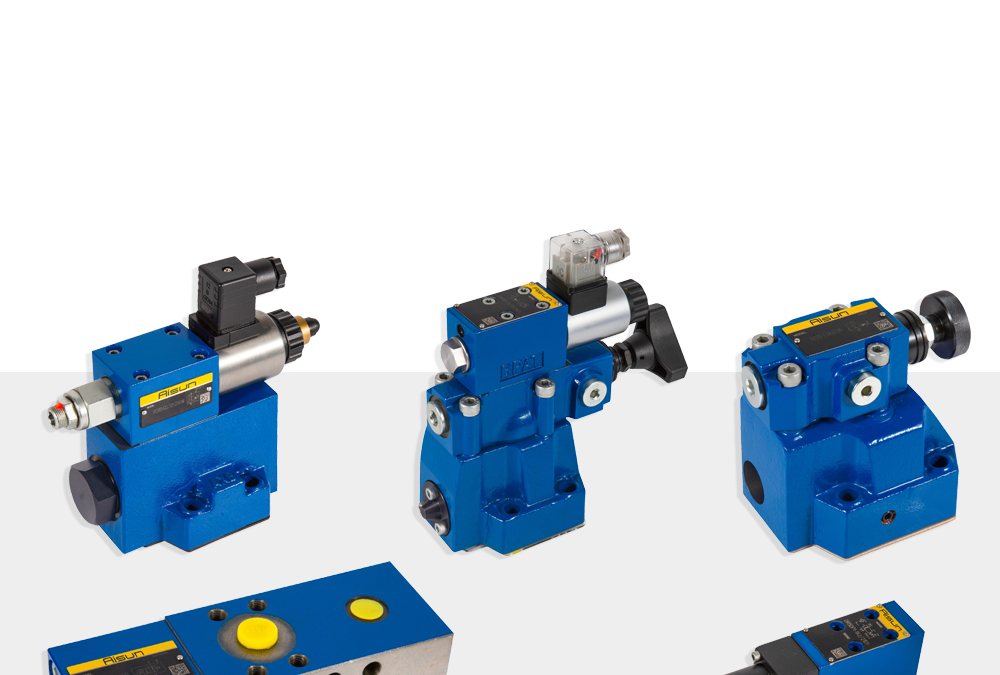
Types of Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic valves are categorized based on their function and application into several main types:
- 1. Directional Control Valves
These valves control the direction of fluid flow. They can direct fluid to different parts of the system or stop the flow entirely. Types of directional control valves include:
– Check Valves: Allow fluid flow in only one direction.
– Spool Valves: Change the direction of flow between multiple paths.
- 2. Pressure Control Valves
These valves regulate and limit system pressure. Types of pressure control valves include:
– Relief Valves: Prevent excessive pressure buildup and protect the system.
– Sequence Valves: Determine the sequence of component operations.
– Pressure Reducing Valves: Reduce pressure in specific parts of the system.
- 3. Flow Control Valves
These valves regulate the amount of fluid flow, thereby controlling the speed of system operation. Types of flow control valves include:
– Throttle Valves: Decrease or increase flow.
– Flow Regulators: Maintain constant flow under varying conditions.
- 4. Combination Valves
These valves combine the features of pressure, directional, and flow control valves and are used in complex systems.
Applications of Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic valves are used in a wide range of industries and machinery. Some of their most important applications include:
- 1. Construction Machinery: Used in cranes, bulldozers, and loaders to control arm movements and lift heavy loads.
- 2. Automotive Industry: Found in braking systems, power steering, and automatic transmissions.
- 3. Aerospace: Used in landing gear control, braking systems, and rudder movement in aircraft.
- 4. Marine Industry: Employed in ship steering systems and anchor mechanisms.
- 5. Military Applications: Used in military equipment such as tanks, artillery, and lifting systems.
- 6. Manufacturing Industry: Applied in plastic injection molding machines, hydraulic presses, and automated production lines.
Advantages of Hydraulic Valves
- 1. Precise Control: Enables accurate regulation of flow, pressure, and fluid direction.
- 2. Durability and Reliability: Hydraulic valves are robust and long-lasting due to their sturdy construction.
- 3. Performance in Harsh Conditions: These valves perform well under extreme environmental conditions, such as high or low temperatures.
- 4. Versatility: Different types of valves are designed for various applications.
Disadvantages and Challenges of Hydraulic Valves
- 1. High Cost: The design and manufacture of hydraulic valves are often expensive.
- 2. Sensitivity to Contamination: Fluid contamination can cause malfunctions or improper operation of the valves.
- 3. Regular Maintenance Requirements: Valves require periodic maintenance and repairs to maintain optimal performance.
- 4. Temperature Effects: Valve performance may be affected by very high or low temperatures.
Technological Advancements in Hydraulic Valves
With technological advancements, hydraulic valves have undergone significant improvements. Some of these advancements include:
- 1. Use of Advanced Materials: Incorporation of stronger and lighter materials to enhance durability and reduce weight.
- 2. Electronic Control Systems: Integration of hydraulic valves with digital and smart control systems (such as IoT) to improve precision and efficiency.
- 3. Energy-Efficient Designs: Development of valves that reduce energy consumption.
- 4. Reduced Environmental Impact: Research aimed at minimizing pollution caused by fluid leaks and improving recyclability.
Conclusion
Hydraulic valves, as key components of hydraulic systems, play a critical role in controlling and optimizing the performance of industrial machinery and equipment. Despite their significant advantages, such as precise control, durability, and versatility, these valves face challenges like high costs and the need for regular maintenance. With ongoing technological advancements, the future of hydraulic valves promises further improvements in efficiency, cost reduction, and minimized environmental impact.